Understanding Modem Routers: A Comprehensive Guide


Intro
When it comes to the world of networking, modem routers play a crucial role that is often overlooked. Picture this: you're in the middle of an important video call or streaming your favorite show, and out of nowhere, the internet drops. Frustrating, right? Understanding how modem routers work can make a difference between smooth sailing and a rough ride in our increasingly connected lives.
Modem routers serve as the gateway that connects your devices to the internet. They translate data coming from your Internet Service Provider into a format that your home network can understand. This process allows your smartphones, laptops, tablets, and smart appliances to communicate seamlessly while also ensuring a consistent connection to the web.
In this exploration, we'll break down the various types of modem routers available, delve into their functionalities, and outline their significance in everyday life. By the end, you’ll have a solid grasp on how these devices operate and why they matter in our digital age.
Types of Modem Routers
Understanding the various types of modem routers can help you select the right one for your needs. Here’s a brief overview of the most common types:
- DSL Modem Routers: These are designed to connect to a DSL internet service. They work by converting digital data from your provider into analog signals and vice-versa.
- Cable Modem Routers: Typically used with cable internet service, these devices take the broadband signal from cable TV lines and modulate it for internet use.
- Fiber Modem Routers: With the advent of fiber-optic technology, these routers can handle massive amounts of data, providing very high speeds.
- Integrated Modem Routers: These devices combine a modem and router into one unit, simplifying setup and reducing clutter.
Each type comes with its own set of advantages, and the choice mainly hinges on what type of internet service you subscribe to.
Key Functionalities
A modem router is not just a piece of hardware; it incorporates several key functionalities that enhance your internet experience. Here are some notable features:
- Network Security: Modem routers come with built-in security measures such as firewalls and WPA encryption, keeping your network safe from unauthorized access.
- Quality of Service (QoS): This feature allows users to prioritize bandwidth for specific activities such as gaming or video streaming, ensuring minimal disruption during peak times.
- Dual-Band Capability: Many modern modems can operate on both the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands. This flexibility helps manage multiple devices at once without sacrificing performance.
- Remote Management: Some routers allow for remote management through applications. Users can control settings and monitor device connections even when not on the home network.
Key Components
Understanding the basic hardware components of a modem router can enrich your knowledge further. Here's what you typically find:
- WAN Port: This port connects your modem to your ISP.
- LAN Ports: These connect local devices like computers and printers to your network.
- Wireless Antennas: For wireless communication, antennas help transmit and receive signals.
- Processor and RAM: Like a computer, the processing power and memory capacity of a router can influence speed and performance.
It's fascinating how these components come together to create a reliable internet experience, isn't it?
"A modem router isn't merely a box; it's the bridge between digital chaos and the streamlined connectivity we often take for granted."
Epilogue
The significance of understanding modem routers goes beyond just knowing how to plug them in. With the growing demand for reliable internet access, recognizing the types, functionalities, and components of these devices prepares you to tackle any connectivity issues that may arise. If you've learned a few things here, just know that you're on the right path to mastering your home network setup. As we continue exploring deeper into the functionalities of these devices, it’ll become clear how integral they are in today’s service-driven world.
Resources for Further Learning
If you want to dive deeper into modem routers and networking, check out these resources:
Taking the time to learn about modem routers can lead not only to better internet performance but also empower you to make proper decisions regarding your networking needs.
What is a Modem Router?
Understanding what a modem router is is fundamental to grasp networking technology. At its core, a modem router is a device that combines two important functionalities into one unit – that of a modem and a router. This consolidation not only contributes to a streamlined user experience but also saves space and reduces the number of devices needed for internet connectivity at home or in an office.
As we continue to rely heavily on internet access for our day-to-day activities, be it streaming, gaming, or remote work, recognizing the capabilities of a modem router becomes crucial. Here, we’ll delve deeper into its components, functionality, and significance.
Defining Modem and Router
A modem is essentially the gateway to the wide world of internet. It translates the signal coming from your Internet Service Provider (ISP) into data that your devices can understand. Think of it like an interpreter for your internet connection. If you have DSL, cable, or fiber broadband, the modem takes those signals and converts them into usable data.
On the flip side, a router is designed to distribute this internet connection to various devices within your network. It acts like a traffic cop, directing data to the right devices, so multiple users can access the internet simultaneously without interference. You could say that the modem kicks open the door to the internet, while the router invites all your devices in.
In summary, while both devices are crucial in establishing internet connectivity, their roles are distinct. The modem tackles the external side of the connection, and the router handles the internal networking, allowing multiple devices to communicate efficiently.
The Combined Functionality
When modem and router functionalities are combined into a single device, convenience reigns supreme. Rather than juggling two separate pieces of hardware, users enjoy a cleaner setup and simplified management. This means less cabling and fewer configurations needed during installation.
Moreover, modem routers often come packed with additional benefits:
- Cost-Effective: Buying one device instead of two can typically save some cash.
- Ease of Use: Setup is often more straightforward, making it user-friendly for those who might not be as tech-savvy.
- Space Saving: With a single device, you get to keep your tech area uncluttered.
- Integrated Features: Many modem routers include built-in security measures, such as firewalls and parental controls, which aid in creating a safer browsing environment.
While there are advantages to using a modem router, it’s essential to consider specific needs. Sometimes separate devices might offer enhanced functionality or performance, especially in larger households or demanding usage scenarios. However, for most users, a well-chosen modem router provides a solid foundation for a robust internet connection.
How Modem Routers Work
In a world where connectivity is king, understanding the inner workings of modem routers is essential. These devices act as the gateway to the internet, facilitating communication between your home network and the vast expanse of data available online. They do much more than connect your devices; they manage data traffic, optimize speed, and ensure security. This section will explore the mechanisms behind modem routers, laying a solid foundation for a more informed usage.
Basic Operation Principles
To grasp how modem routers function, one must first understand their fundamental principles. The essence of a modem router lies in two critical operations: modulation and routing.
- Modulation refers to the process of converting digital data from your devices into a form suitable for transmission over various media, be it coaxial cables in cable modem routers or optical fibers in fiber-based models. This modulation happens swiftly, allowing the seamless transfer of information to and from your internet service provider (ISP).
- Routing, on the other hand, deals with directing this data efficiently. Once your modem router receives data from the internet, it must choose the correct destination within your local network. It does this using a set of rules and protocols that dictate how data packets are managed. The routing functionality ensures that your request for a webpage doesn't end up in the wrong "house" on the data highway.
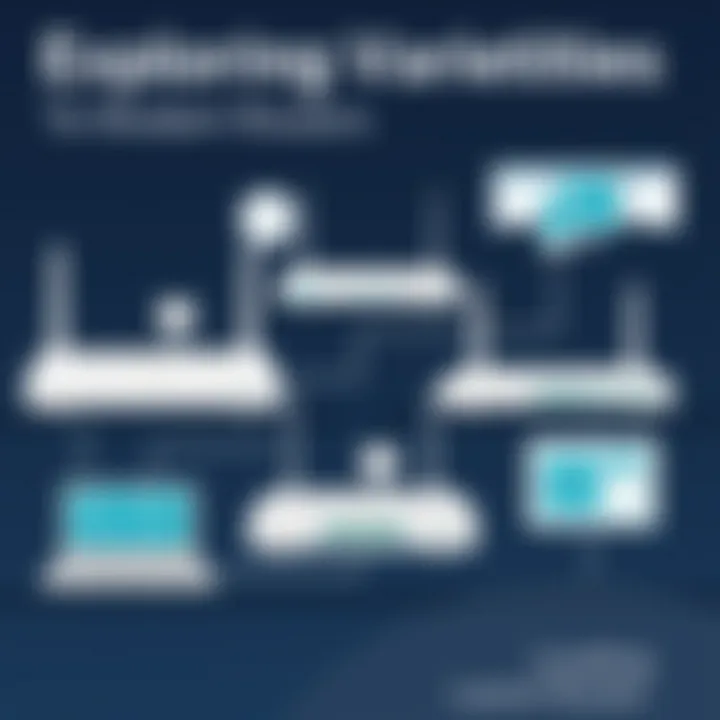
When you send a request, perhaps for loading your favorite video, the modem router quickly converts that request into a signal, travels through the internet, fetches the data, and routes it back to you. This fine balance of modulation and routing embodies the basic operation principles of modem routers.
Data Transmission Processes
Transitioning from operation principles to the actual data transmission processes, it's vital to focus on two main components: upstream and downstream data flow.
- Upstream Flow: This process involves sending data from your devices to the internet. For instance, when you are uploading a file, your device sends this information to the modem router. It then modulates that data into a suitable format before directing it to your ISP. Think of it as sending a letter through a postal service where your modem router is the post office ensuring your mail gets to the right place.
- Downstream Flow: Conversely, this pertains to receiving data from the internet. When you access a website, the data travels in the opposite direction. Before reaching your device, this incoming data packet undergoes a demodulation process, converting it back into a format that your devices can understand. The speed and efficiency of this process can be influenced by various factors such as ISP limitations, network congestion, and router specifications.
Furthermore, modem routers utilize various technologies like PPPoE and DHCP for managing connections. PPPoE (Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet) allows multiple users to share a single broadband connection by addressing each connection individually. On the other hand, DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) automatically assigns IP addresses to devices in the network, simplifying connectivity management.
Understanding these data transmission processes sheds light on the intricate ballet that happens within a modem router as it dances between various devices and the infinite world of information on the internet. With this knowledge, users can better appreciate their modem routers and perhaps identify issues hindering efficient internet performance.
Types of Modem Routers
When it comes to establishing a robust internet connection, the type of modem router you choose can make a world of difference. The landscape of modem routers is vast, each designed to cater to specific needs and enhance user experiences. Understanding the kinds available aids users in making informed decisions, whether they be casual surfers or those who delve into tech-intensive tasks. Here, we’ll explore four pivotal types of modem routers: DSL, Cable, Fiber, and Wireless, each with its unique set of characteristics, advantages, and considerations.
DSL Modem Routers
DSL (Digital Subscriber Line) modem routers are a popular choice for those living in areas where cable connections might not be available. This type of modem router uses existing telephone lines to whiz through data at relatively high speeds, even while allowing phone communication simultaneously. An important consideration is that the speed tends to decrease the further away you are from the service provider’s central office.
- Advantages:
- Considerations:
- Cost-effective for users in rural areas.
- Offers decent speeds suitable for surfing, streaming, and casual gaming.
- Installation is straightforward, often manageable by the user without professional help.
- Speed limitations compared to cable or fiber options.
- Quality of service can fluctuate based on distance from the central office.
Defining characteristics of DSL modem routers include ADSL and VDSL technologies, each providing different levels of speed and performance. ADSL typically is slower but adequate for basic usage, while VDSL offers much higher speeds, making it more fitting for heavy internet activities.
Cable Modem Routers
Cable modem routers utilize the same network infrastructure as your cable TV, allowing installers to provide simultaneous internet and television services. This type shines particularly in urban areas where cable broadband facilities are abundant, allowing multiple users to connect with reliable speeds.
- Advantages:
- Considerations:
- Generally faster than DSL and suitable for families with multiple devices.
- Reliable connection during peak hours since the bandwidth can support high usage.
- Typically requires a subscription to cable service to function.
- If you're in a crowded area, speeds might slow down during high-demand periods, as signals can become congested.
Cable modem routers offer configurations that can support high-speed plans, handling everything from online gaming to streaming in 4K without a hitch. Look for models that support DOCSIS 3.0 or 3.1 standard for optimum performance.
Fiber Modem Routers
Fiber modem routers represent the zenith of internet technology at present. By using light from fiber-optic cables, these devices offer unparalleled speeds and bandwidth. If available in your area, opt for fiber as it enables faster downloads and smoother streaming experiences.
- Advantages:
- Considerations:
- Blazing fast speeds – up to 1 Gbps or more.
- Symmetric download and upload speeds, which is invaluable for content creators or remote workers.
- Availability is often limited to certain geographical areas, mainly urban centers.
- Usually comes at a premium compared to DSL and cable options.
Fiber connections are particularly suitable for smart homes with multiple devices that require high bandwidth. It's also ideal for cloud computing and other data-heavy applications.
Wireless Modem Routers
Wireless modem routers introduce flexibility and convenience, allowing users to connect their devices without a physical connection. These devices often support both wired and wireless capabilities, making them versatile for modern home setups.
- Advantages:
- Considerations:
- Mobility allows easy connection of smartphones, tablets, and other Wi-Fi-enabled devices.
- Easier to set up in homes without the hassle of cables running everywhere.
- Signal strength can be affected by walls, distance, and interference from other devices.
- Security risks are higher without adequate protections like WPA3.
Wireless modem routers cater to a range of functionalities, from standard home usage to advanced gaming setups, depending on their specifications and enhancements such as dual-band support and MU-MIMO technology.
Key Components of a Modem Router
Understanding the key components of a modem router is essential for anyone looking to grasp how these devices power our Internet connectivity. It's not just about having a box that connects to the wall; it’s the symphony of hardware and software working together that allows us to surf, stream, and stay connected. Each component plays a critical role, contributing to the overall performance, reliability, and security of our network. Let's break down these components and realize why they matter.
Modulation Technology
Modulation technology is essentially the backbone of how data is transmitted over various mediums. It converts digital data from your computer into signals suitable for transmission over phone lines, coaxial cables, or fiber optics. Different types of modulation techniques, such as Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM) or Pulse Amplitude Modulation (PAM), have varying effects on speed and efficiency.
For example,
- ADSL (Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line) uses modulation to convert digital data into signals for DSL lines, enabling faster download than upload speeds.
- DOCSIS (Data Over Cable Service Interface Specification), which is prevalent in cable modem routers, utilizes sophisticated modulation techniques that allow multiple channels to transmit data concurrently, enhancing speed.
Investing time to understand modulation technology not only helps in troubleshooting issues but also aids in selecting the right modem router for specific internet plans.


Networking Ports
Networking ports are the gatekeepers of data flow in and out of your modem router. Each port serves a purpose, and understanding them is crucial for setting up a robust network.
- Ethernet Ports: These are standard for wired connections. A modem router may have multiple Ethernet ports, commonly used to connect devices like desktop computers, gaming consoles, or smart TVs directly to the router for a stable, high-speed connection.
- USB Ports: Many modern modem routers come equipped with USB ports. These allow you to share files from an external hard drive or connect a printer to your network, making it accessible from any device.
Also worth noting, some modems offer VoIP ports for voice communication or WAN ports for connecting to external networks. Recognizing how many and what types of ports a device has can help you effectively utilize your modem router, tailoring your network to your needs.
Firmware and Software
Firmware and software are the unsung heroes of modem routers, governing everything from performance to security. The firmware is a specialized form of software that provides the control program for the modem router.
Regular updates to the firmware are incredibly important. These updates fix bugs, patch security vulnerabilities, and sometimes even improve overall functionality. Users often overlook this step, assuming their device is fine as is, but neglecting firmware updates can expose you to various security threats.
There's also configuration software that interfaces with the modem router. This software can be found within the router’s web portal, allowing users to adjust settings, manage device access, and monitor network activity. Familiarity with this software means you can customize your experience, optimizing performance and enhancing security protocols as needed.
"The right modem router, when understood down to its components, can revolutionize how we interact with technology daily."
To equip yourself for a successful networking experience, grasping these components is indispensable. This knowledge empowers you to make informed decisions, ensuring your modem router effectively meets your unique internet needs.
Installation of Modem Routers
Getting a modem router up and running might seem straightforward, but there are crucial steps in the process that can significantly impact your overall experience. A proper installation ensures not only a reliable internet connection but also lays the groundwork for optimizing the performance of your network. Missteps during the initial setup can lead to connectivity woes that linger long after the boxes have been unpacked. Therefore, understanding the installation process is vital, especially for users navigating the complex world of modem routers for the first time.
Preparation for Setup
Before diving into the setup process, take stock of your tools and equipment. This might seem trivial, but having the right gear at hand can smoothen the entire experience. You'll need your modem router, power adapter, Ethernet cables, and a computer or smartphone to interface with the device. Additionally, it's wise to check for any updated firmware from the manufacturer’s website to ensure that you are working with the latest features and security protocols.
Next, consider the placement of your modem router. The placement affects the wireless signal strength. Ideally, you’ll want to situate the device elevated and centrally located in your home or office to maximize coverage.
To sum up:
- Gather necessary equipment: modem router, power adapter, and Ethernet cables.
- Check for firmware updates to ensure your device is equipped with the latest features.
- Strategize placement for optimal coverage and signal strength.
Configuration Process
After setting the scene for a successful installation, it's time to configure your modem router. Start by connecting the power adapter to the device and plugging it into a power outlet. With the device powered on, it's time to connect it to the internet. If you're using a DSL or cable connection, attach the appropriate Ethernet cable from your wall jack to the modem router's WAN or Internet port.
Once everything is connected, grab your computer or smartphone. Connect to the modem router via an Ethernet cable or wirelessly by selecting the router's SSID from your device’s Wi-Fi settings. Typically, the default network name and password can be found on a label attached to the device.
After connecting, launch a web browser and enter the router's IP address, which is often or . Following this, you'll be prompted to enter the administrative username and password. Once you've completed this step, you’ll gain access to the router’s dashboard.
Now, navigate through the settings.
- Change the administrator password to something strong and memorable.
- Configure the Wi-Fi settings: This includes setting the network name (SSID) and password.
- Enable security features like WPA3 where possible for enhanced protection.
Finally, save your settings and reboot the router for the changes to take effect. Each modem router may differ slightly in its interface and configuration options, so don't hesitate to consult the user manual or online resources if needed.
"A device well-set is a device well-used."
Preparation and configuration might initially seem tedious, but taking these steps thoughtfully ensures a robust foundation for your home or office network. Mastering the installation lays the groundwork for proficient network use and troubleshooting in the future.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
As with any technological device, modem routers are not without their challenges. Understanding how to troubleshoot common issues is crucial for any user wishing to maintain optimal internet connectivity. When modem routers malfunction or underperform, it can disrupt our day-to-day activities, whether they involve work, communication, or leisure. Addressing these problems promptly can enhance the overall experience and prevent minor hitches from escalating into bigger headaches.
Connectivity Problems
Achieving a stable connection can feel like chasing a moving target sometimes. It’s no surprise that connectivity issues top the list of woes that users encounter. Several factors can lead to these frustrating problems. Often, it’s as simple as unplugging the modem router, waiting a spell, and plugging it back in again. However, if that doesn’t do the trick, other issues might be at play.
Here are a few coefficients to consider:
- Wiring Issues: Loose cables, damaged ports, or connectors can create interruptions. Checking the physical connections can reveal discrepancies.
- ISP Problems: Your internet service provider might be experiencing outages. It’s wise to check their status page or reach out directly.
- Network Congestion: Too many devices hogging bandwidth might lead to connectivity drops. Reducing the number of connected devices can sometimes ease the load.
Being proactive about these common hiccups can often save a lot of time and frustration.
Slow Internet Speeds
Having a fast-paced life means you want everything around you to move briskly – including your internet. Slow internet speeds can significantly hinder productivity, whether streaming, gaming, or simply browsing. Diagnosing the root cause of sluggishness can be quite a task.
Here are some pointers to consider when tackling slow speeds:
- Bandwidth Limitations: Ensure the chosen internet package meets your usage needs. Package speeds might be suitable for browsing, but streaming multiple devices could require more.
- Outdated Equipment: Utilizing older modem routers can bottleneck speeds. Ensure your device supports current standards like DOCSIS 3.1 or Wi-Fi 6 to maximize potential.
- Interference: Wireless signals can easily be disrupted by walls, furniture, or other electronic devices. Try relocating your modem router to a more central location or using ethernet cables for the devices needing a stable connection.
Addressing slow speeds requires a mix of strategic planning and practicality, ensuring your connection remains reliable and quick.
Overheating and Performance Drop


Like us, electronic devices can overheat under pressure, leading to performance drops. It's typically unexpected when your reliable modem router begins to show signs of fatigue. Overheating can stem from two main culprits: environmental factors and usage overload.
Here’s how you can manage these concerns:
- Ventilation: Ensure your modem router is in a well-ventilated space. Avoid hiding in cabinets or spaces with little airflow since limited air circulation can trap heat.
- Routine Maintenance: Dust buildup can block vents, so cleaning the device occasionally helps in maintaining performance. Use a soft cloth or compressed air to clear out any dust particles.
- Usage Patterns: If you are demanding a lot from your connection, especially during peak hours, it might be wise to stagger high-usage activities to reduce strain.
Being attuned to these factors can minimize overheating issues and maintain a steady performance throughout the day.
Remember that a well-functioning modem router is your gateway to an efficient digital world. Taking the time to troubleshoot can yield substantial benefits.
Comparing Modem Routers with Separate Modems and Routers
In today's tech-savvy landscapes, understanding the differences between modem routers and standalone devices has become increasingly important for anyone who's looking to enhance their internet experience. It's not just about having speed; it's about making an informed choice that suits individual needs. This section dives into the core of this comparison, bringing clarity to each side of the debate, whether you are a budding coder or someone trying to optimize a home network.
Advantages of All-in-One Devices
Modem routers combine both the modem and the router into one sleek device. This might seem like just a matter of convenience, but the benefits extend far deeper. Here are some key advantages:
- Space-Saving Design: Having a single unit takes up less room, reducing clutter.
- Simplicity of Setup: Configuring one device is often easier and quicker. Many users can simply plug it in and go without the hassle of integrating two separate devices.
- Cost-Effective: Sometimes, buying an all-in-one can be cheaper than purchasing two separate units, as companies often bundle their products.
- Optimized Compatibility: With one manufacturer overseeing both modem and router functionalities, you're less likely to encounter compatibility issues. This ensures smoother performance and simplified troubleshooting.
As a result, for individuals who want plug-and-play ease and less equipment hassle, an all-in-one modem router may be the optimal choice.
When to Choose Separate Devices
On the flip side, there are folks who may prefer to set up their networks with separate modem and router devices. Choosing this route can offer several distinct advantages worth considering:
- Superior Performance: High-end routers often outperform modem routers, especially when it comes to extensive coverage or multiple simultaneous connections.
- Upgradability: If technology advances or your needs change, it might be easier to upgrade just one part of your setup. For instance, you could replace your router without needing to touch the modem.
- Customization Options: Separate devices can offer more extensive features such as advanced security protocols, custom firmware, or enhanced parental controls, which can be beneficial for both personal and family use.
- Specialized Functions: For tech enthusiasts or gamers, having separate devices allows for finer adjustments to those unique requirements through a more specialized equipment choice.
"Understanding your needs first can save you a world of headaches later on the network front."
For more insights on networking options and products, you may explore further at Wikipedia or Britannica for a well-rounded understanding of how these devices function together in modern-day connectivity.
Security Considerations
In the realm of modem routers, security considerations hold a high stake. As we navigate the digital landscape, threats such as hacking, data breaches, and malware have become commonplace, making it essential to prioritize the protection of our home networks. With the rise of remote work, online banking, and smart home devices, understanding how to safeguard one’s network against potential vulnerabilities is paramount. The topic of security not only enables users to maintain privacy but also enhances the overall performance and trustworthiness of their internet-connected environments.
Understanding Security Protocols
To fortify a network, it is crucial to understand the various security protocols employed in modern modem routers. This entails knowing the standards for keeping data safe during transmission. Here are some key protocols:
- WPA2/WPA3: These Wi-Fi Protected Access protocols help encrypt data, making it harder for unauthorized users to eavesdrop. WPA3, the latest in the line, offers additional security features, such as protection against brute-force attacks.
- IPSec: Usually applied in Virtual Private Networks (VPNs), this protocol encrypts data at the IP level, safeguarding information as it travels over a network.
- SSL/TLS: Used extensively on websites, these protocols ensure that data exchanged between your browser and a web server is encrypted, further building trust during transactions.
By implementing these protocols, users establish a solid foundational layer for network security. Moreover, staying updated on newer versions and enhancements is equally vital, as cyber threats evolve constantly.
Implementing Safeguards
After grasping the significance of security protocols, the next step involves implementing concrete safeguards to minimize risks. Here are a few tangible measures you can adopt:
- Change Default Credentials: Often, modem routers come with generic usernames and passwords. It’s wise to replace these with strong, unique credentials to prevent unauthorized access.
- Regular Firmware Updates: Manufacturers frequently release updates that patch vulnerabilities. Regularly checking for and installing these updates can make a significant difference.
- Enable Network Encryption: Always use the highest level of encryption available. This not only protects your data but also adds layers to your network’s defenses.
- Utilize Firewalls: Hardware or software-based firewalls work as barriers between your network and potential threats. Ensure that the built-in firewall on your modem router is enabled.
- Guest Networks: If guests need to connect to your Wi-Fi, set up a separate guest network. This keeps your primary network secure while allowing others to access the Internet.
"An ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure."
In the case of networking, investing time and resources into these security measures could ultimately save you from severe consequences down the line. Maintaining a proactive stance in securing your modem router not only supports the integrity of the devices connected to it but also cultivates a more reliable and resilient online experience.
For more detailed insights and guidelines on network security, you can visit resources like Wikipedia or NIST's Guidelines.
Future Trends in Modem Router Technology
As we venture into an era where connectivity defines our daily lives, staying abreast of future trends in modem router technology becomes imperative. This section focuses on how emerging innovations not only affect the efficiency of internet access but also redefine our interaction with digital tools and smart appliances. In a world increasingly reliant on high-speed internet and seamless communication, understanding these trends helps users anticipate their future needs and make informed decisions about their networking setups.
Advancements in Speed and Connectivity
Gone are the days when a simple dial-up connection ruled the world. The demanding nature of modern applications means today’s users require substantial internet speed. Fortunately, advancements in modem router technology are ushering in a new wave of possibilities. Recent developments bring us technologies like DOCSIS 4.0, which promise to elevate cable internet speeds to mind-boggling levels, reaching up to 10 Gbps. Isn’t that astounding?
Additionally, the introduction of Wi-Fi 6 significantly enhances both speed and connectivity. By optimizing bandwidth management, it allows several devices to operate smoothly at the same time. This means no more waiting when multiple devices are streaming movies, playing online games, or working from home.
Some notable features of these advancements include:
- Increased Bandwidth: Connections can manage more data without congestion.
- Lower Latency: Users experience quicker response times, which is vital for gaming and video conferencing.
- Enhanced Range: Improved signal strength ensures coverage in larger areas, even with obstacles like walls.
This brings us to the salient point of user experience. The more reliable and faster the connection, the less frustrated users will be in their daily activities. Thus, as modem routers become increasingly capable, they help us keep our lives running smoothly.
Integration with Smart Home Devices
With the burgeoning rise of smart home technology, modem routers are evolving beyond mere internet connectivity. They are at the heart of interconnected systems within homes, serving as the hub for devices ranging from smart speakers to security cameras. The integration of these devices into modem routers hints at a seamless user experience that will likely dominate the future landscape.
For instance, the amalgamation of smart home devices with enhanced modem router technology allows users to control lighting, temperature, and even security systems with a single command through their smartphones or voice control systems. No more juggling multiple apps or devices; it's all about convenience now.
Consider these critical benefits of integration:
- Centralized Control: Manage all smart devices from one interface, reducing complexity.
- Energy Efficiency: By coordinating device schedule, users can conserve energy effectively.
- Upgrade Potential: As new devices emerge, users can integrate them without changing their entire technology setup.
“The future is about making life more manageable. A smart modem-router setup is where connectivity meets convenience.”
Moreover, security protocols in these integrated setups are not to be overlooked. With devices communicating frequently, having a solid defense against unauthorized access becomes even more crucial. As such, selecting a modem router that prioritizes security offers peace of mind in addition to high-speed connectivity.







